Rabies is one of the most terrifying diseases to afflict animals because of how it is spread, its lack of treatment and its dramatic clinical presentation. The virus is spread by bites of infected animals. Within the salivary glands, the virus replicates and enters the saliva. When a rabid animal bites, the virus is inoculated […] Read more
Stories by Jamie Rothenburger, DVM

Microchips are an effective animal identification tool
Microchips are the gold standard for lifelong, permanent animal identification. These tiny electronic transponders are the approximate size of a grain of rice and are enclosed in a thin cylinder of glass. They sit just under the skin and are inert, meaning the body is not stimulated to reject them or wall them off. Veterinary […] Read more
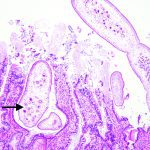
Tapeworm infections on the rise in people and dogs
In a recent column, I discussed new research by myself and colleagues at the University of Calgary that identified a deadly tapeworm parasite in wild muskrats. A reader suggested I expand on the human and dog aspect of this emerging disease. Just to briefly recap, the parasite is a tapeworm known as Echinococcus multilocularis. Animals […] Read more
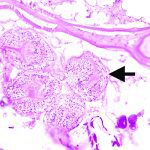
New study shows emerging parasite also infects muskrats
Human and pet dog cases of a deadly parasitic disease have recently increased in Western Canada. In Alberta, the parasite Echinococcus multilocularis has been diagnosed in 17 people between 2013 and 2020. In pet dogs, there were 27 cases in Western Canada between 2009 and 2021 with 18 of those occurring in Alberta. This is […] Read more

Veterinarians kept horses healthy during First World War
Several years ago, when helping my uncle Walter sort through some DVDs, we came across a copy of A Bear Named Winnie, a CBC Television movie. He gave me the DVD and I watched it with awe. This CBC production tells the true story of Canadian veterinarian Dr. Harry Colebourn. While I’d seen the images […] Read more

Procedures in place for animal research
An enormous range of animal species are used in research for a variety of reasons. There is the familiar use of animals as models for human diseases, which is where the white laboratory mice and rats come in. Scientists may also study animals for their own benefit. It is worth considering the reasons we use […] Read more

Avian influenza infection spreads to wild mammals
The global outbreak of H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus, continues. With the arrival of autumn, migrating wild birds may continue to spread, contract and die of this infection. Avian influenza has historically been considered a pathogen of birds. Wild waterfowl such as ducks carry it without significant clinical disease. They are also thought […] Read more

Vital maternal bonding process starts during pregnancy
From what we can tell, dinosaurs didn’t do much of it. Neither do many modern-day reptile, amphibian and bird species. But mammals certainly invest significant time and food resources into rearing young. And the foundation for this critical behaviour is the maternal bond. For wild mammals, the strong bond between dam and offspring is essential […] Read more

Dramatic cases from vet school show cattle’s resiliency
I left the hallowed halls of the Western College of Veterinary Medicine at the University of Saskatchewan 13 years ago and embarked on my career as a veterinarian. Reflecting on this passage of time, most of which I spent in the practice of pathology, there are some weird and interesting cattle cases that stand out. […] Read more
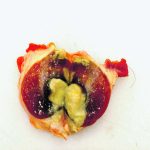
Lymph nodes are a critical part of the immune system
Lymph nodes are present throughout the body and are an important part of the immune system in animals. Their main function is to drain and monitor lymph from specific locations in the body. Lymph, also known as lymphatic fluid, is a liquid that forms from normal leakage of microscopic blood vessels in tissues. It is […] Read more




